/reboot/media/95268e66-9e53-11ed-b306-0242ac14000b/6aef1564-a71b-11ef-b18e-0242ac120013/1-1-design-sans-titre-37.png)
Indoor drone inspection: how does it work?
Interior inspection by drone is establishing itself as an innovative and essential solution in many industrial sectors. Designed to overcome the limitations of traditional methods, it combines precision, speed and safety, even in the most confined environments. How does indoor drone inspection work? What types of drone are used, and what are the steps involved? This article provides a detailed overview of this revolutionary technology and its many applications.
Why use a drone for indoor inspections?
Inspections in confined environments represent a technical and logistical challenge. Tunnels, tanks, ducts or reservoirs are often difficult to access, requiring specialized tools and rigorous safety protocols. The use of a balloon drone makes it possible to meet these challenges, while delivering key benefits.
Firstly, the drone replaces the need to send operators into risky areas, significantly reducing workplace accidents. Secondly, drones offer great inspection flexibility, capturing high‑resolution images and video in real time, even in inaccessible areas. Finally, it is possible to produce a 3D model in post‑processing.
Technological advances, such as the Stereo2, further optimize these inspections with innovative features such as stabilization, dust resistance and powerful lighting.
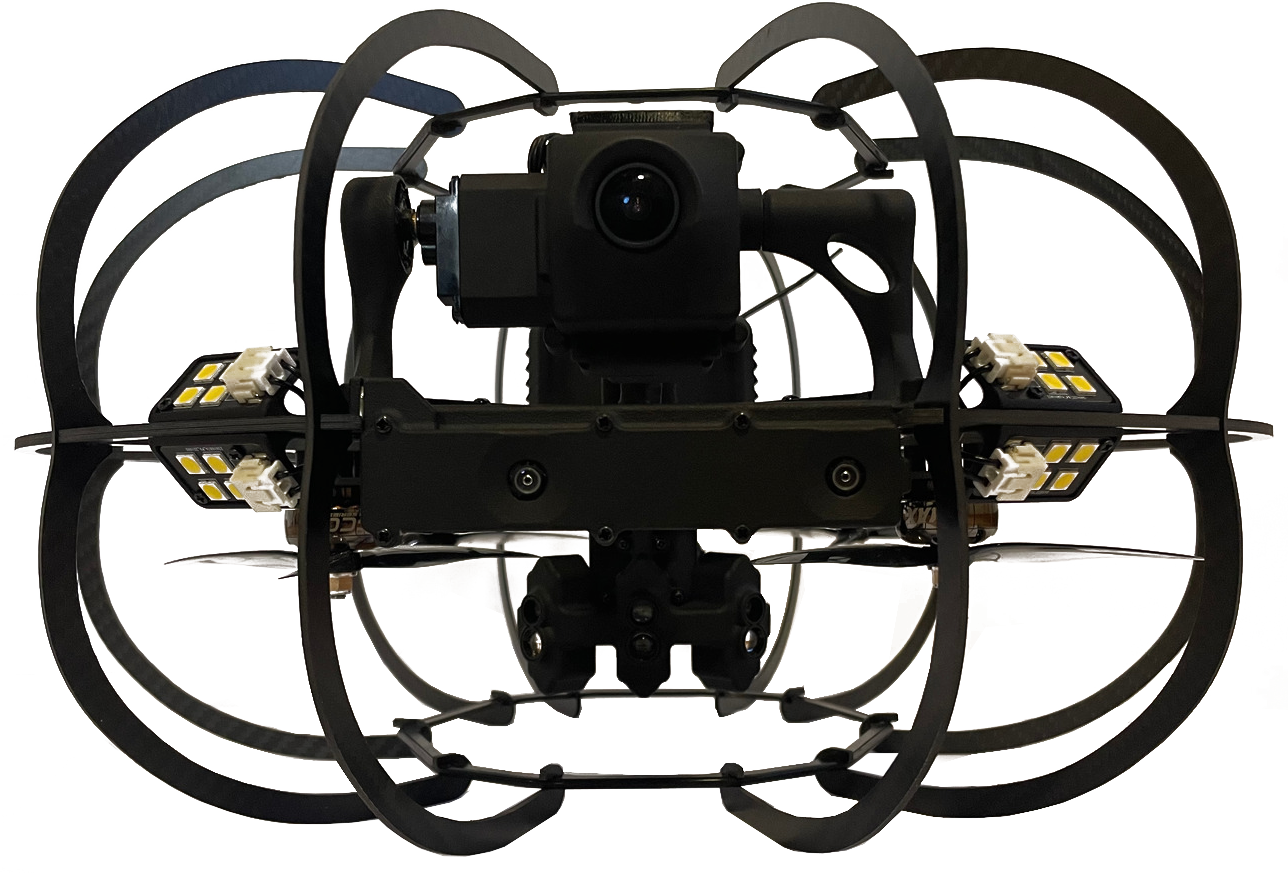
What types of drone are used for indoor inspections?
Indoor drone inspection requires equipment specifically designed to navigate in confined environments. Here are the main categories of drone suitable for these missions:
1. Small drones
Compact ball drones are ideal for tight spaces where optimum maneuverability is essential. Their small footprint enables them to fit into tight passages while maintaining great agility.
2. Drones with protective cage
Carbon cage drones are ideal for environments where collisions with walls are frequent. The cage not only protects the drone from damage, but also allows it to bounce off surfaces without interrupting the mission. This is particularly useful in ducts and tanks where obstacles are numerous.
3. Focus on the Stereo2
The Stereo2 is a flagship model in the field of indoor drones. Compact, robust and technologically advanced, it combines several key features to guarantee quality inspections. Equipped with a protective cage and stabilization system, it can operate efficiently even in dusty or poorly‑lit environments. Its powerful lighting and assistance modes enable it to maintain a precise distance from surfaces, ensuring reliable, detailed data collection.
Key stages in indoor drone inspection
An indoor drone inspection follows a methodical process to guarantee efficiency and safety. Here are the main steps:
1. Preliminary site assessment
Before any intervention, a detailed analysis of the site is carried out. This includes identification of critical areas, potential obstacles and environmental conditions. It enables us to anticipate challenges and define mission objectives.
2. Mission planning
Planning is a crucial step in optimizing drone deployment. It includes defining flight paths, points of interest to be inspected, and the technical parameters required for mission success.
3. Safety checks
Before starting the inspection, rigorous checks are carried out. This includes the condition of the drone (battery, sensors, propulsion systems), as well as site conditions. This step guarantees not only the safety of the operators, but also the integrity of the equipment.
4. Inspection execution
During the execution phase, the drone is piloted remotely by experienced operators. Thanks to its advanced features, like those of the Stereo2, the drone captures images and videos in real time, while respecting planned trajectories.
5. Data analysis
Once the inspection is complete, the data collected is transferred for in‑depth analysis. This data can include HD images, detailed videos, or even 3D models. It is used to assess the condition of inspected structures and identify any anomalies.
Fields of application for indoor drone inspection
Indoor drone inspection can be adapted to a variety of industrial sectors. Here are just a few examples of real‑world applications:
Petrochemical industry
Drones are used to inspect tanks, pipelines and vessels, reducing the need for extended shutdowns. They can accurately detect corrosion, cracks or other damage.
Power plants
In thermal and nuclear power plants, drones monitor turbines, chimneys and ventilation ducts. Their ability to operate in complex environments makes them indispensable for regular inspections.
Marine sector
Ship holds, tanks and internal compartments can be inspected quickly and efficiently thanks to drones, avoiding laborious and costly procedures.
Mining and cement industry
Drones inspect tunnels, silos and other hard‑to‑reach areas, even in dusty environments. Their powerful lighting and robustness enable them to meet these challenges without compromise.
Public infrastructure
Drones play a crucial role in the inspection of bridges, road tunnels and urban pipelines, providing detailed diagnostics for maintenance.
The added value of indoor drone inspection
Indoor drone inspections represent a major advance in industrial and technical infrastructure management. Their ability to operate in dangerous or inaccessible environments improves worker safety while reducing operational costs. What's more, drones like the Stereo2 guarantee accurate, usable results by capturing HD images.
By adopting this technology, companies benefit from an innovative, fast and reliable solution for monitoring and maintaining their facilities. Whether in the petrochemical, marine or mining industries, indoor inspection drones are becoming an essential tool for meeting growing performance and safety requirements.
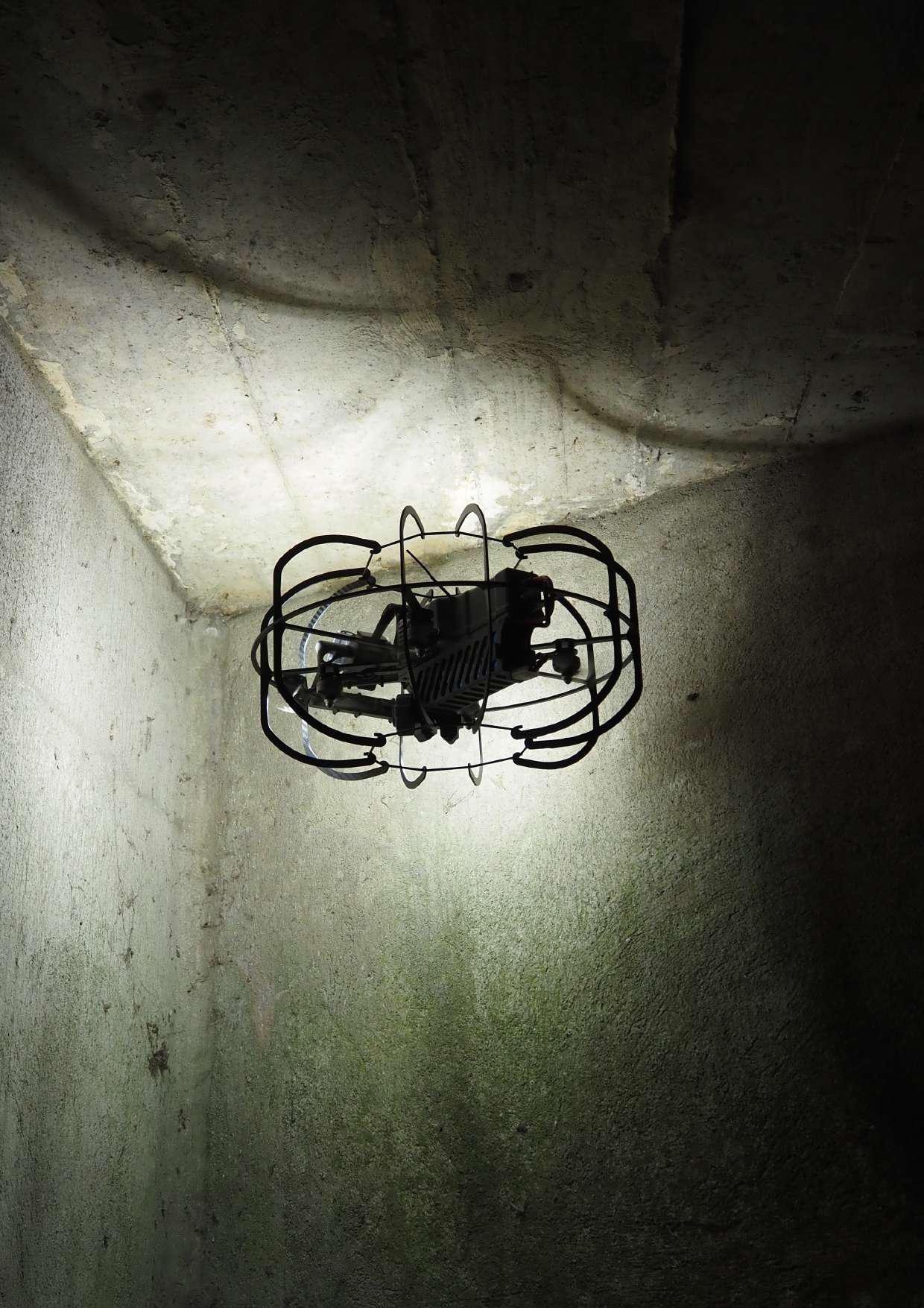

With tools like the Stereo2, the future of indoor inspection looks bright. Investing in this technology means choosing efficiency and safety, while paving the way for proactive infrastructure management.
:strip_exif()/reboot/media/95268e66-9e53-11ed-b306-0242ac14000b/7e1d7cf8-a2df-11ed-b843-0242ac14000b/1-1-multinnov-pour-fond-blanc.png)
:strip_exif()/reboot/media/95268e66-9e53-11ed-b306-0242ac14000b/7e1d7cf8-a2df-11ed-b843-0242ac14000b/1-1-multinnov-pour-fond-blanc.png)
/reboot/media/95268e66-9e53-11ed-b306-0242ac14000b/dc1f8834-9c28-11ef-8036-0242ac120013/1-1-design-sans-titre-31.png)
/reboot/media/95268e66-9e53-11ed-b306-0242ac14000b/e450df62-9de5-11ef-8deb-0242ac120013/1-1-capture-d-ecran-2024-11-08-103326.png)
/reboot/media/95268e66-9e53-11ed-b306-0242ac14000b/2410fe10-8e8e-11ee-b27d-0242ac12000c/2-2-pipe-inspection.jpg)